 |
Catalogs
Cepheid Phys. Properties
Binary Cepheid Solutions
Projects
SB2 Cepheids
Classical Cepheids
Type II Cepheids
Papers
by category
by first author
by target
Visitors so far: 97041.
Relevant publication:
2018, ApJ, 862, 43 (← click to see the publication at ADS/arXiv)
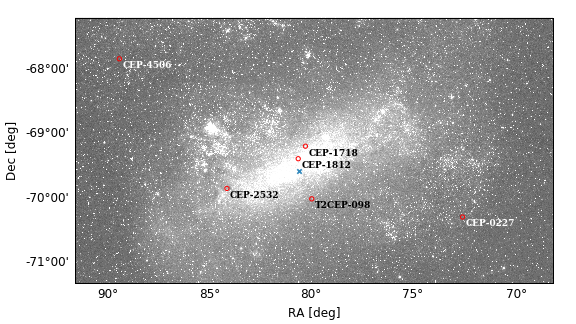
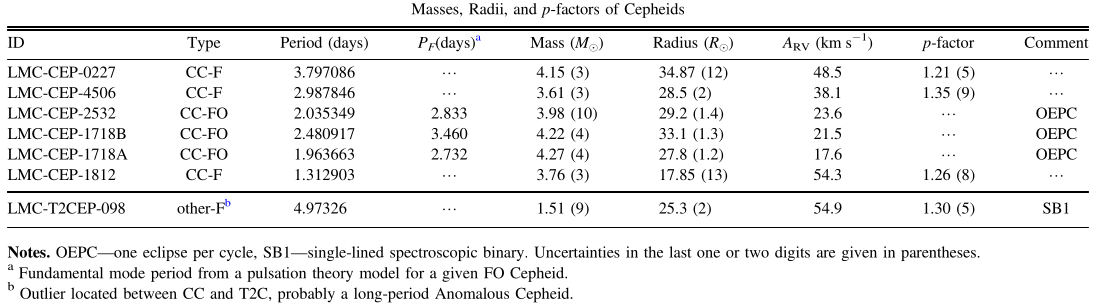
Based on new observations and improved modeling techniques, we have re-analyzed seven Cepheids in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Improved physical parameters have been determined for the exotic system OGLE-LMC-CEP-1718 composed of two first-overtone Cepheids and a completely new model was obtained for the OGLE-LMC-CEP-1812 classical Cepheid. This is now the shortest period Cepheid for which the projection factor is measured. The typical accuracy of our dynamical masses and radii determinations is 1%.
 |
|---|
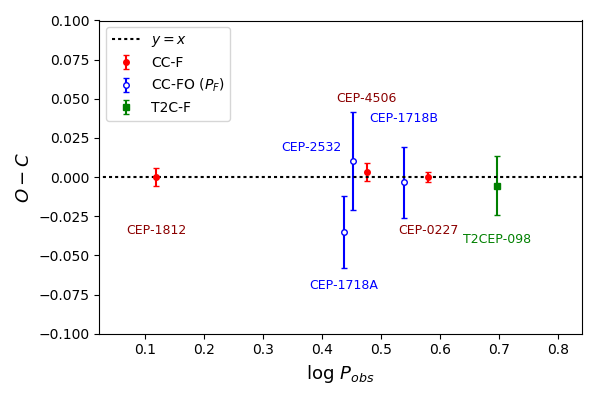
The radii of the six classical Cepheids follow period-radius relations in the literature. Our very accurate physical parameter measurements allow us to calculate a purely empirical, tight period-mass-radius relation which agrees well with theoretical relations derived from non-canonical models:
log PMR = -1.555(35) - 0.795(44) log M + 1.703(23) log R
 |
|---|
This empirical relation is a powerful tool to calculate accurate masses for single Cepheids for which precise radii can be obtained from Baade-Wesselink-type analyses. The mass of the Type-II Cepheid κ Pav, 0.56 ± 0.08 M☉, determined using this relation is in a very good agreement with theoretical predictions.
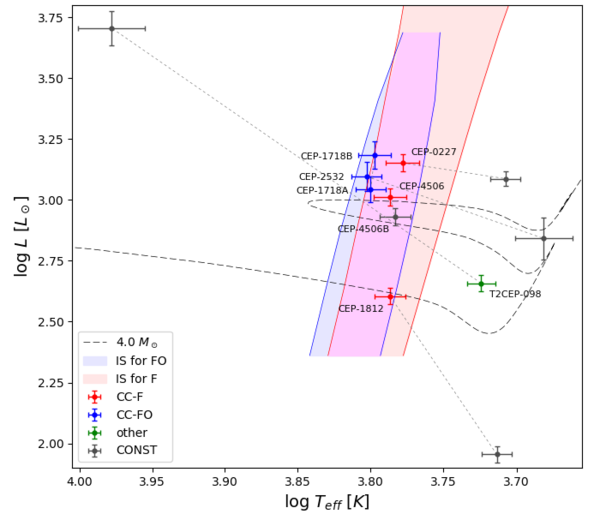
We find large differences between the p-factor values derived for the Cepheids in our sample. Evidence is presented that a simple period--p-factor relation shows an intrinsic dispersion, hinting at the relevance of other parameters, such as the masses, radii and radial velocity variation amplitudes. We also find evidence that the systematic blueshift exhibited by Cepheids, is primarily correlated with their gravity. The companion star of the Cepheid in the OGLE-LMC-CEP-4506 system has a very similar temperature and luminosity and is clearly located inside the Cepheid instability strip, yet it is not pulsating.
 |
|---|